26/01/2016
 |
| Left-to-right: Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin - the crew of Apollo 11. |
Introduction: 25th August, 2012 marked the
death of Neil Armstrong, the first man to ever set foot on the moon back
in 1969. This man, along with his "Apollo 11" crew-members, Buzz Aldrin
and Michael Collins, is among the true heroes of the scientific era.
However, owing
to the work of several notable conspiracy theorists, there exists
a huge mob of people that believes that none of the moon landings the
Apollo missions were real. To uphold their claims, they
present a variety of arguments, ranging in quality from utter dumb to
moderately technical - however all of these arguments can be proved
false with a
little logic and scientific knowledge. The theories are based on
insufficient knowledge.
Since I
have always been an astronomy freak and can't see one great hero
presented in such bad light, I decided to write a huge article debunking
all the major theories in one place - a service rendered in the honour
of Neil Armstrong.
-------------------------------------------------------------------
How the conspiracy theories started:
On February 15, 2001 the FOX television aired a program titled "Conspiracy Theory: Did We Land On The Moon?". The
program featured "evidence" that proved NASA's Apollo missions were
faked. (i.e. they were shot in a studio on Earth, supposedly by the
director of film The Space Odyssey)
Although the conspiracy theories had been around for decades, starting in 1974 with Bill Kaysing's book "We Never Went to the Moon", reinforced by the works of the award-winning photographer David Percy (author of Dark Moon: Apollo and the Whistle-Blowers) and Ralph Rene (author of " NASA Mooned America!") but the airing of this program was the time when most people started believing in them.
But why do moon landing conspiracy-theories exist in the first place? Are the theorists credible?
If I were to give an opinion on why such theories exist - assuming the theorists had no negative motives - I would simply suggest that these theories arose out of lack of scientific knowledge. Most of the notable theory advocates were people not trained in science (e.g. Bill Kaysing held an arts degree; David Percy was a photographer; Ralph Rene was self-taught publisher with no formal degree) These people made conclusions based on analysis of Apollo photographs and footage, with little or none attention towards the complex physical SCIENCE involved in the moon's environment. People who have knowledge of science can better judge the physics involved in the moon missions instead of people who have insufficient or no knowledge of physics.
--------------
DEBUNKING THE SPACE "ODDITIES" PRESENTED BY THE CONSPIRACY THEORISTS:
We
shall now examine the many claims made by various conspiracy theorists
and debunk them with LOGICAL and SCIENTIFIC facts. We shall start off
with points raised by the leading advocates and move on to the other
ones when they're done.
1. The PHOTOS shows wind blowing the U.S. flag on the moon, although the moon has no
atmosphere and the flag should not blow on the moon (Ralph Rene)
Reply: This is perhaps the most commonly repeated point from the theorists. It is quite absurd to make a decision on MOVEMENT in a STILL photograph. Obviously, the people seem to be perceiving the wrinkles on the flag as signs of motion - and I would recommend them to watch all the video footage and note that the flag is actually motionless.
If you search for Lunar Flag Assembly, you will note that the flag was fastened to a Г-shaped rod
so that it did not hang down (see photo on the left).
Now
for some proof, see the photos below, the two photos are two successive
photographs showing Buzz Aldrin saluting the US flag. The flag is motionless although the wrinkles on the flag appear to be indicative of motion.
 |
| These two photographs had a time difference of several seconds |
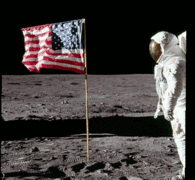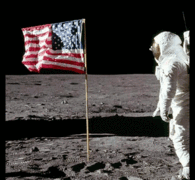 |
| Animation of the two photos, showing that though the camera moved between the photographs, the flag is motionless. |
(Also see the video footage in point no. 10, it clearly shows a motionless flag)
2. There is also a VIDEO footage of the astronauts that shows that the flag was moving (Raplh Rene)
Reply: The
video Raplh mentioned is the one in which Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin are
trying to hoist the US flag into the moon soil. Take a look at the
video below, keeping in mind the structure of the flag post that I
mentioned above.
As you can see,
the flag is not moving of it's own accord. It's moving because the
astronauts are twisting the flagpole, trying to hoist it into the
ground. The movement of the flag is unlike anything you would see on
earth. In the absence of air, there is no damping effect on the flag
and it keeps fluttering due to inertia. On earth, the movements of the
flag would quickly be damped.
NOTE: This was also EXPERIMENTALLY verified by MythBusters in Episode 104 of their TV series using this method: "The Build Team placed a replica of the American flag planted on the Moon
into the vacuum chamber. They manipulated the flag in a manner similar
to what the astronauts did when they planted the flag on the Moon, then
stopped the manipulation. They first tested at normal pressure; the
momentum moved the flag around somewhat but quickly dissipated. In pure
vacuum conditions, after the manipulation stopped, the momentum
caused the flag to flap wildly as if it were being blown by a breeze.
This is because there was no resistance from air to dampen the motion.
This proved that in a vacuum, a flag does not need wind to flap for a
while after a person sets it in motion."
3.
Without an atmospheric cloud cover, there should have been a sky full
of stars but Apollo photographs do not show a starry sky (Bill Kaysing,
Ralph Rene). NASA could not hope to recreate the lunar sky, so they may have opted
for simple black backdrops.
Reply: Faking
a starry sky is too easy a task for any studio. The fact that there are
no stars actually proves the authenticity of the photographs.
 |
| Capturing stars requires slow shutter speeds of >30s for good exposure and can not be captured at fast shutter speeds. |
Those who are familiar with photography might know that capturing stars requires the camera to be set at SLOW SHUTTER SPEED to maximize exposure. For properly capturing a starry sky on earth, an average of 30 seconds time should be set.
The white surface of the moon was strongly reflecting the sunlight. In such strongly lit situations, a FAST SHUTTER SPEED ranging around 1/500 seconds may be required to prevent overexposure. Apollo photographs were taken at fast shutter speeds. However, at this configuration, stars can definitely not be captured.
 |
| This is an example of a space photograph in which no stars are seen; the photograph was captured at fast shutter speed to minimize overexposure resulting from the Earth's glare due to sunlight. |
4. The
film used by astronauts on the moon should have melted due to the supposed high
levels of radiation and temperature above 250 ° F (Bill Kaysing)
Reply: There are several points to be noted here.
- A special transparency film produced by Eastman Kodak under a NASA contract was used by the Apollo astronauts. The photosensitive emulsions layers were placed on an ESTAR polyester film base. The melting point of ESTAR is 490° F, although some shrinkage and distortion can occur at around 200° F.
- The films were protected in special camera casings to keep them cool and were never exposed to high temperatures.
- The moon has no air, hence, without convection or conduction, the only method of heat transfer on moon was radiation. Radiative heat can be effectively directed away from an object by wrapping it in a material with a reflective surface, usually simply a white material. The camera casings, as well as the astronauts' cooling system-equipped clothing, were indeed white.
5. Only two men walked on the Moon in every Apollo mission. Yet the astronaut reflected in the visor is not holding a camera.
Who took the shot?
 |
| Apollo 12 Astronaut: Bean's camera is attached to his suit. |
Reply: Astronauts
were not "holding" their cameras like we do. The cameras were attached
to the chest of the space-suit they were wearing, leaving their hands
free for other operations unless they wanted to click.
Here is a close-up photo that shows the camera to be attached to the suit.
6.
Shadows cast on the moon's surface should be parallel (and equal) as
there is only one light source - the sun. Yet in some photographs, the
shadows cast by the astronauts are not parallel.
Reply: This is explained on the basis of perspective of the camera and the angle of photography. In addition, the surrounding hills and slopes should also be taken into account as they alter the direction of light. One such example was experimentally demonstrated by MythBusters (read caption for details)
As far as perspective and angle of photography is concerned, shadows that are parallel in real life may appear different in a photograph. The image below illustrates this concept.
 |
| This photograph shows the "perspective" concept. The shadows are infact parallel in real-life but in a 2D angular photograph, may give a false impression of not being parallel. |
7.
The shaded
side of objects should be dark and in sharp contrast, but they are
not, indicating a three point lighting in a studio (Ralph Rene)
 |
| Buzz Aldrin is clear - despite being in shadow |
&
8. Many Apollo photographs show lighting
"hot spots", as well as a darkening of the surface toward the horizon.
Sunlight should not produce hot spots, nor should the surface fade in an
airless environment. Seemingly, a spotlight was used.
Reply: The soil of the moon has a strong tendency to reflect sunlight. The (main) reason is that there are tiny glass spheres present in the soil that were formed in meteorite impacts.
As a result of strong reflection from the soil, even the shaded sides
of objects are not dark.
(The moon surface reflects 10% of the total light it receives. When the sun is directly overhead, the maximum illumination can be up to 10,000 lumens. However, in the Apollo missions, the sun was diagonal, and the luminosity was hence decreased to 3400 lumens. Now, when 10% of it will be reflected, the moon surface will seem to be lit up with 340 lumens power - the power roughly equal to a 35 watt light bulb.)
The "hot spots" also result from similar phenomenon. Contrast enhancement from NASA in some shots also created more of this effect. As for fading of the surface, the surface fades drastically toward the horizon. It is brightest near the foreground due to sunlight being preferentially reflected back toward the camera. Farther away, the sunlight is preferentially reflected away from the camera, making the ground look dark. The technical term for this phenomenon is Heiligenschein, and is the result of light refraction, reflection, and diffraction on the surface of and inside the glass spheres of the lunar soil. (This phenomenon can also be seen on wet grass where water droplets act like small glass spheres).
(The moon surface reflects 10% of the total light it receives. When the sun is directly overhead, the maximum illumination can be up to 10,000 lumens. However, in the Apollo missions, the sun was diagonal, and the luminosity was hence decreased to 3400 lumens. Now, when 10% of it will be reflected, the moon surface will seem to be lit up with 340 lumens power - the power roughly equal to a 35 watt light bulb.)
The "hot spots" also result from similar phenomenon. Contrast enhancement from NASA in some shots also created more of this effect. As for fading of the surface, the surface fades drastically toward the horizon. It is brightest near the foreground due to sunlight being preferentially reflected back toward the camera. Farther away, the sunlight is preferentially reflected away from the camera, making the ground look dark. The technical term for this phenomenon is Heiligenschein, and is the result of light refraction, reflection, and diffraction on the surface of and inside the glass spheres of the lunar soil. (This phenomenon can also be seen on wet grass where water droplets act like small glass spheres).
9. During the videos of the
lunar landings the astronauts replied instantly to Mission Control in
Houston. Yet light, radio waves, and all energies of the electromagnetic
spectrum travel at roughly 186,000 miles per second, meaning the response time
of the astronauts to comments made by Mission Control should have been a little
over two seconds since the moon is over 200,000 miles from the Earth.
Reply: This is actually a pretty great point put forward by one theorist online; however it clearly shows lack of information.
NASA hadn't established a direct link with the television channels. The live pictures transmitted from the Moon
were displayed on a 10-inch black-and-white monitor and a vidicon camera
was pointed at the screen, the output of which was given to the channels.
Television
channels actually showed us the live footage from the ASTRONAUT's side.
i.e. the voices of the mission control that we heard in the footage
were coming to us from the moon, and not directly from mission control.
The conversation between the mission control and the astronauts as seen
in the footage was hence, without any time delays.
10. There is one photograph of an astronaut standing on the
surface of the Moon in direct sunlight, yet he casts no shadow
 |
| Theorists mention the absence of a shadow in this photograph. |
Reply: The photograph the theorists refer to is shown. If you see carefully, you will note that there is a shadow below him and to his right.
The shadow is not attached to his body as the astronaut John Young was jumping. A video of that scene is shown below. It is odd that the theorists do not have information about such a popular scene.
(P.S. Don't mind the music in the video: Just watch it as I couldn't find any better version :P And do observe the motionless flag)
11. In an Apollo 11 photograph of Buzz Aldrin the horizon is
located at eye level; however, if the camera was mounted to Neil
Armstrong's chest, the horizon should be at chest level.
 |
| Note the level of the horizon in this shot. |
Reply: The
theorists refer to the image shown and argue that the horizon should be
at chest level if the camera that took this shot was at chest level.
However they assume that Buzz and Armstrong were standing at the same level. If
Armstrong's reflection in Buzz's visor is enlarged, Armstrong will be
seen to have the horizon at his chest level - indicating that he
actually was standing at a higher level than Buzz when the photo was
taken. Armstrong's chest, and hence the camera, was at Buzz's eye level, which is why the horizon is seen at Buzz's eye level.
 |
| Enlargement of Armstrong's image in Buzz's visor, indicating that Armstrong was indeed standing at a higher level than Buzz. |
12. The
sound of the Lunar Module descent engine should be heard in the Apollo
audio transmission, but there is no sound heard, not even at touchdown.
Reply: This one is pretty easy. sound transmission requires a
medium. On earth, the engines would surely make alot of noise but in the
vacuum atmosphere of the moon, with no air to act as a medium, sound
should not be heard.
13. A clear footprint cannot be made in vacuum because there is no moisture to hold its shape.
Reply: This point was also experimentally disproved by the MythBusters.
Our planet's soil is weathered and rounded,
so the particles do not support each other's weight very well unless some moisture is present. Lunar
soil, because it is not weathered, has a more jagged texture, so the
particles "lock" with each other and will hold the shape of the imprint
much more clearly.
14. One
photo from Apollo 11 is looking up at Neil Armstrong about to take his
first step on moon. If Armstrong was the first man on the Moon, then who
took the shot? (Ralph Rene)
Reply: This
is among the most non-objective points. Surprisingly however, it came
not from a curious child pondering over the moon landings but from Ralph
Rene himself.
If
I plan a trip with a big moment, obviously I will be fully equipped to
capture that big moment in the perfect way. NASA, similarly, had a plan
for it's big moment.
While still on the steps, Neil Armstrong deployed the Modularized
Equipment Stowage Assembly from the side of the Lunar Module, which happened to contain the TV camera. That camera took the photograph under question.
15.
The space suits were too heavy and too pressurized for the astronauts
to comfortably perform all the tasks that they did. The gloves
on the Apollo space suits would also have expanded in the vacuum of
space to
the point where they would be immobile. (Ralph Rene)
Reply: The space
suit although made of hard materials has jointed sections to allow a
good range of movements.
The upper and lower torso sections are put on separately and the two
pieces are
connected at the waist to allow the flow of water and gas-lines. Gloves
and helmet create a sealed protection against meteoroids and
radiation. The material they are made of does not expand in vacuum, it's
made for vacuum and low-pressure environments.
As far as weight is concerned, the
suits are really heavy for Earth but in space (gravitation-free
environment) and Moon (low-gravity environment), weight of the suit is
none, and negligible, respectively.
16. The Lunar Lander weighed 17 tons and the
powerful booster rocket (of 10,000 lbs thrust) at the base of the Lunar Lander was fired to slow
descent to the moons service. Yet it has left no traces of blasting on the dust
underneath. It should have created a small crater, yet the booster looks like
it's never been fired.
Reply: The
Lunar Lander certainly had a huge mass but with the moon's low gravity -
a 6th of Earth's gravity, the 17 ton would actually have weighed 17/6 =
2.8 tons. That certainly isn't enough to leave a crater at the landing site; aided by the fact that the lunar soil particles "lock" with each other (as mentioned in point 10 above).
Moreover:
- The Lunar Module was throttled down to mere 3000 lbs when landing, and turned off before actual touch down.
- The Lunar Module descended at an angle, moving laterally across the ground. When the astronauts identified a suitable landing site, the LM leveled off and dropped to the surface. The LM did not hover over its final landing site for any significant length of time.
- In a vacuum exhaust gases expand rapidly once exiting the engine nozzle. They should not create a "pressure effect".
17. A large amount of dust was generated during the landings, yet no dust can be seen on the Lunar Module footpads or anywhere.
Reply: This is because in the absence of atmosphere, the dust particles generated in landing simply followed a ballistic motion when they were blown away. On moon, we can not get those "billowing dust clouds" like Earth since there is no air to suspend the clouds.
18.
The TV footage was hopeless. Part of the reason for the low quality was
that, strangely, NASA
provided no direct link up. So networks actually had to film all the
footage from a TV screen in Houston - a deliberate ploy, so that nobody
could properly examine it. (Ralph Rene)
&
19. By contrast, the still photos were
stunning. Yet that's just the problem. The astronauts took thousands of
pictures, each one perfectly exposed and sharply focused. Not one was badly
composed or even blurred. (Ralph Rene)
Reply: The
transmission of videos from Lunar Module wasn't done a high-speed
internet connection: It used the Lunar Module's radio antenna and power
supply, and was hence limited to a low bandwidth.
Apollo 11 could therefore use a black-and-white, slow-scan TV camera with a
scan rate of 10 fps (frames-per-second) at a low resolution of 320x240.
In order to
broadcast the images to the world, the pictures had to first be
converted to the commercial TV standards. In the US, this was the EIA
standard of 30 fps at 525x394 resolution. This is why the networks had to shoot the footage from NASA's screen in Houston, and not directly.
 |
| A highly underexposed photograph from Apollo. |
As
for the photos, the theorists should note that not all shots were
perfect; but then, why should NASA actually publish unfocused or
improperly
exposed photographs? The photos publicly released were the best photos among the roughly 5300+ photographs from all Apollo missions. The picture shown at the side is an example of an underexposed photo.
20. Some Apollo photographs show mysterious lights in the shadowy background that appear to be studio spotlights.
 |
| Lens flare in this photo is mistaken for studio spotlight. |
Reply: Some
theorists present photographs like the one on the left and claim that
the "lights" seen in the background are studio lights.
However these "lights" are actually lens flare and are often seen on earth as well when the image of sun is reflected back and forth inside the camera lens.
Another close-up image shown below shows the same lights; and from that photo one can clearly infer that the lights are lens flares afterall.
 |
| These lights are clearly lens flares. |
This notorious C rock is shown in the figure. Theorists claim it to be the markings of a studio prop.
This was uncovered to be just a hair fibre that got scanned on the film. The images were widely distributed in this form. The original photos do not have this C.
A magnification of this "C" shows a secondary mark that appears to be a shadow is clearly
visible under the top portion of the mark, which supports the fact that the "C" was a hair fibre on film.
 |
| Note the secondary mark - a shadow. |
22. The Apollo crews were launched into space but never left Earth orbit.
Reply: This
is a very lame argument. An ordinary orbiting satellite, even one that
isn't as large and as white as Apollo, is clearly visible from earth.
People even track them as hobbies. It is known that Soviets also tracked
Apollo all the way from the moon to the earth.
23. To reach the Moon astronauts would have to travel through the Van Allen Radiation Belts, resulting in lethal doses of radiation.
Reply: This
is often stated by the theorists. NASA was well aware of the Van Allen
Radiation belt and upon research, found that there was no danger. The
total radiation dose that the astronauts encountered was 1 REM, an
amount that is easily tolerated by the body. Toxic levels of radiation
begin over 150-200 REM with 300+ accounting for lethal doses.
24. There are many pictures of spacesuited astronauts inside
buildings with artificial moonscapes, presumably the studio where the
moon landings were faked.
 |
| Jim Lovell training for Apollo 13. |
Reply: These
photos are from various training/practice scenarios that all astronauts
were subjected to before being sent to moon. NASA never claimed that
those photos were from moon, nor ever made any attempt to hide them.
They are publicly available.
25. The film of the astronauts moonwalking is actually film of the
astronauts skipping in front of a high frame-rate camera, slowing down
the picture and giving the illusion they are on the Moon. If the video footage of the Apollo astronauts is played at
double normal speed, their motion appears quite normal, thus the images
were faked by playing normal motion at half speed.
Reply: The MythBusters tried this experimentally: "
Adam donned a replica
NASA space suit
and mimicked the astronauts' motions while being filmed by a slow
motion camera. They also attached Adam to wires in order to mimic the
Moon's lower gravity. While comparing the new and original footage, the
MythBusters noted that at first glance, they looked similar, but there
were many small discrepancies due to filming in Earth's gravity. In
order to film in microgravity, the MythBusters boarded a Reduced Gravity
Aircraft run by Zero Gravity Corporation
and filmed exactly the same movements. Adam noted that the movements
were more comfortable and made more sense in microgravity, and the
footage from the plane looked exactly like the original film. The
MythBusters concluded that the Moon landing film is authentic"
Besides, there is a scientific explanation: An object in
free flight will follow a ballistic trajectory in accordance with
Newton's laws of motion.
Moon's gravity is one-sixth that of earth. If the ballistic flight of an object on the Moon is sped up by a factor
of 2.46 it will mimic exactly ballistic motion on Earth.
Apparently,
when using a slow motion camera, the ballistics will resemble, but the
arm movements will seem unnaturally fast - and oddities will appear.
Some points that the theorists can not falsify:
1. There are many moon rocks brought back by the Apollo missions. 382 kilograms (840 lb) of Moon rocks were collected
during the six manned missions. These have characteristics that are not found in Earth or
artificial rocks, such as evidence of meteoroid bombardment and exposure
to cosmic rays. Likewise, Earth rocks have unique characteristics
not found in the moon rocks, such as weathering and exposure to water.
Finally, the moon rocks returned by Apollo have been determined to be
between 3.1 and 4.4 billion years old, older than any rocks on earth.
 | ||
| Genesis rock brought back by Apollo 13 is older than any Earth rocks. |
2. Apollos 11, 14 and 15 erected laser reflectors
on the lunar surface. Laser beams are routinely fired at these
reflectors through telescopes at McDonald Observatory in Texas and near
Grasse in southern France and these laser beams are actually reflected back from the moon. Timings of these reflected beams are used to
measure the Earth-Moon distance to an accuracy of one inch. Do the theorists have any answer to this?
3. In 2009, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft, which was in a low polar
orbit over the Moon, returned a series of images of Apollo landing
sites showing the vessels themselves at rest on the Moon’s surface. A direct visual confirmation is a sure sign that the moon landings were real.
 |
| Apollo 17 landing site photographed by the LRO mission |
4. Last but not the least, a few logical points: More than half a million people were working on the Apollo program. To plan a conspiracy on this scale would have been as difficult as making real landings. It's just not feasible. Yet, after all this time, not a single inside man has slipped anything.
Those who are naturally dead did not make any deathbed confessions or
leave behind any secret incriminating documents or photos. None of the
Apollo workers ever showed any evidence of "reward". They all had quiet
lives in retirement with no luxurious mansions or anything. No
disgruntled employee fired from the Apollo program made any dark
revelations. Everything is so normal and nothing seems fishy.
NVIDIA has recently graphically reconstructed the entire scene of the moon landings using their new Maxwell GPU technology. They carried out extensive research about the surface of the moon, the lights in the environment at the time of the landing and so on. All the necessary factors were taken into account. When the graphics was rendered in 3D, the resultant output was exactly in accordance with the footage and photographs of NASA. Take a look at this photo:
As you can see, this screenshot from NVIDIA's reconstruction of the moon landings using Maxwell GPU is exactly like the photo in point number 7 of this article: Buzz Aldrin was clear despite being in shadow!
THE ABSOLUTE VERDICT:
The above discussion
makes it clear that all the objections raised by the conspiracy theorists were
invalid – MAN REALLY WENT TO THE MOON –
SEVERAL TIMES. It was indeed a great achievement
for mankind and should be remembered as such.
i hope u like the article....






No comments:
Post a Comment